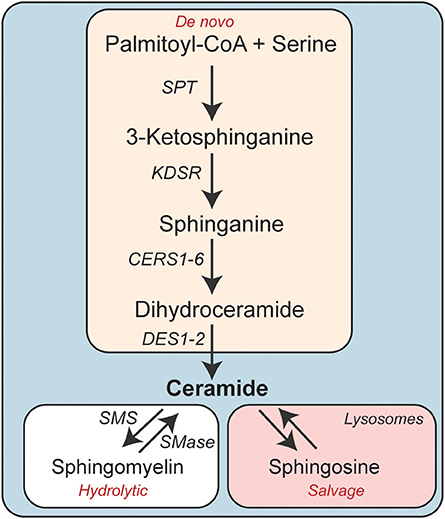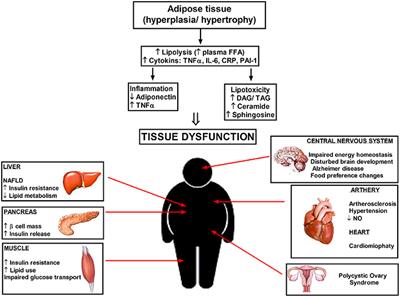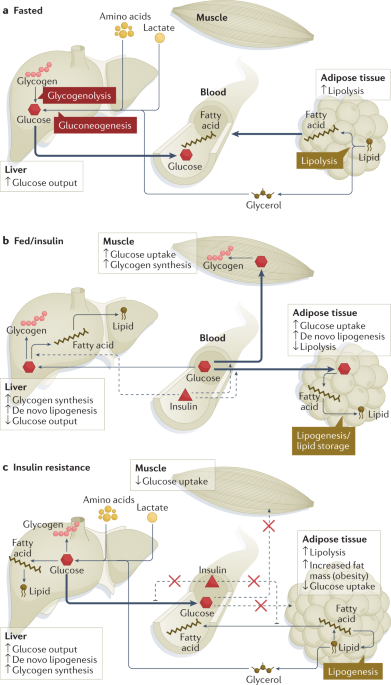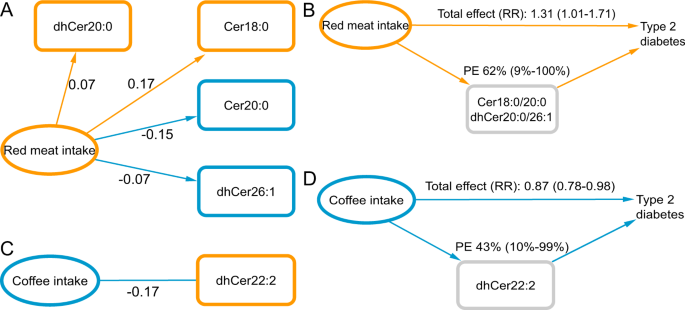
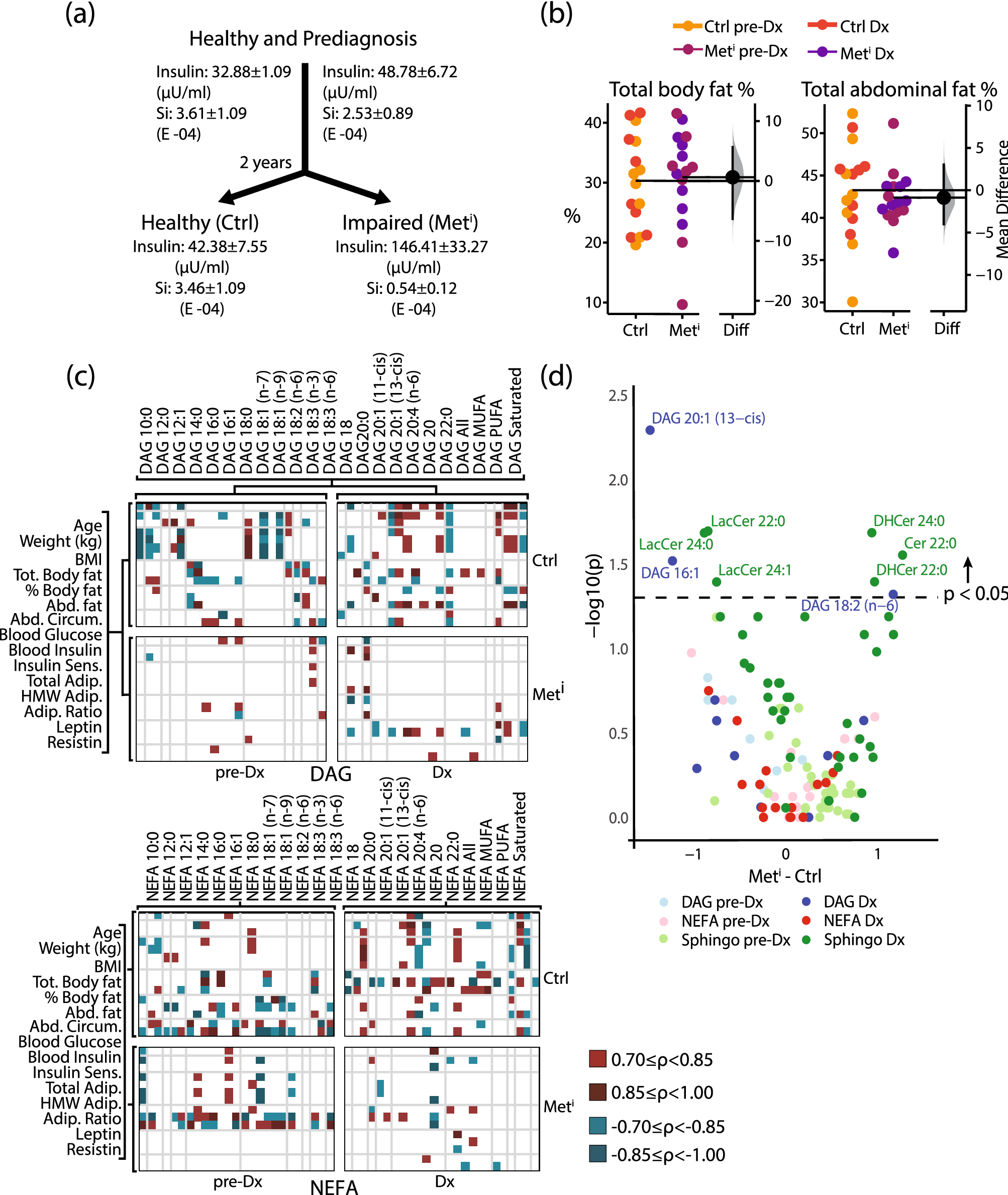
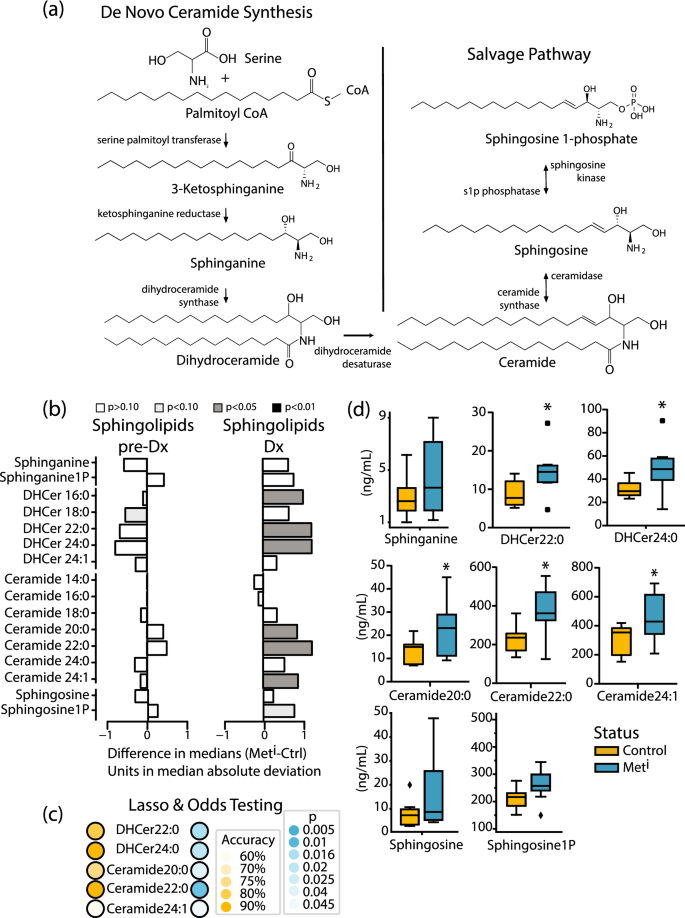
Dihydroceramide- and ceramide-profiling provides insights into human cardiometabolic disease etiology | Nature Communications
Ceramides are early responders in metabolic syndrome development in rhesus monkeys | Scientific Reports
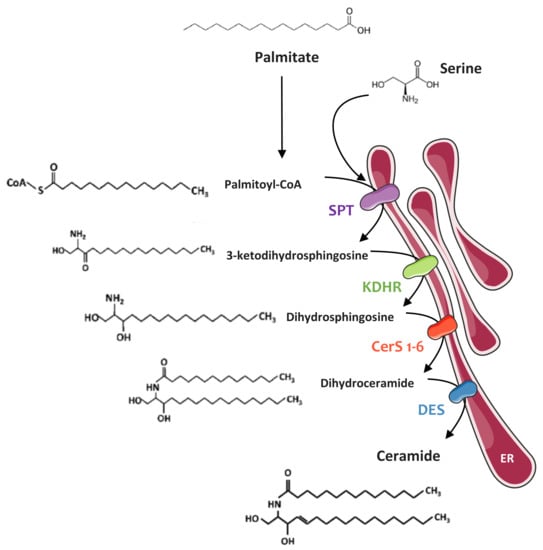
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Sphingolipid Metabolism: New Insight into Ceramide-Induced Lipotoxicity in Muscle Cells

AdipoR agonist increases insulin sensitivity and exercise endurance in AdipoR-humanized mice | Communications Biology

Distinct mechanisms involving diacylglycerol, ceramides, and inflammation underlie insulin resistance in oxidative and glycolytic muscles from high fat-fed rats | Scientific Reports
Ceramides are early responders in metabolic syndrome development in rhesus monkeys | Scientific Reports
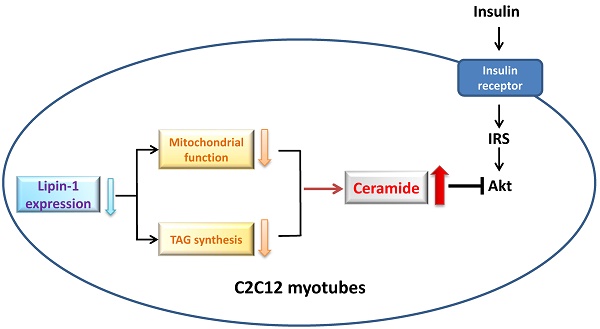
Downregulation of lipin-1 induces insulin resistance by increasing intracellular ceramide accumulation in C2C12 myotubes
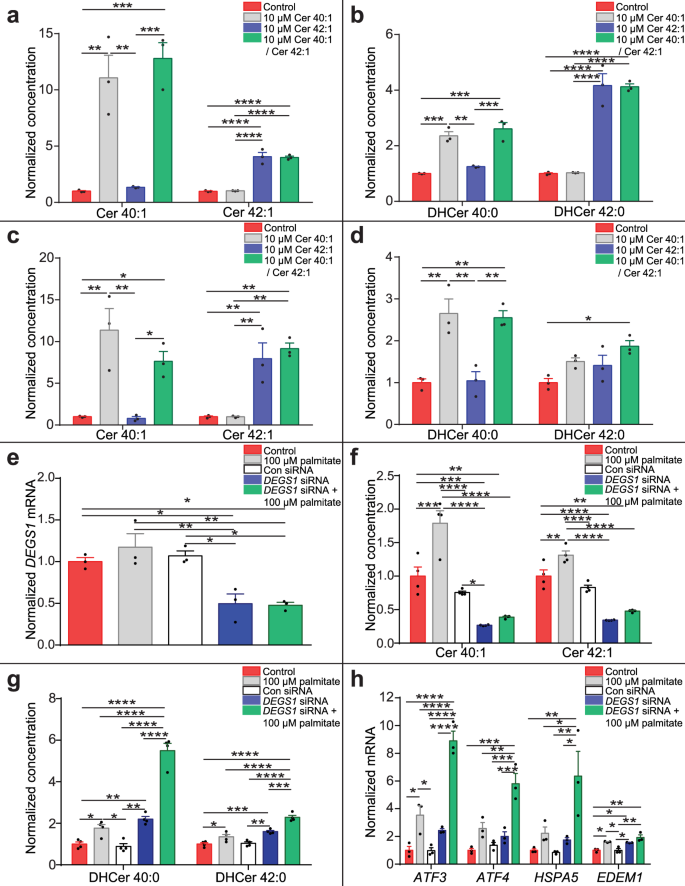
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications

High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance | Nature Communications
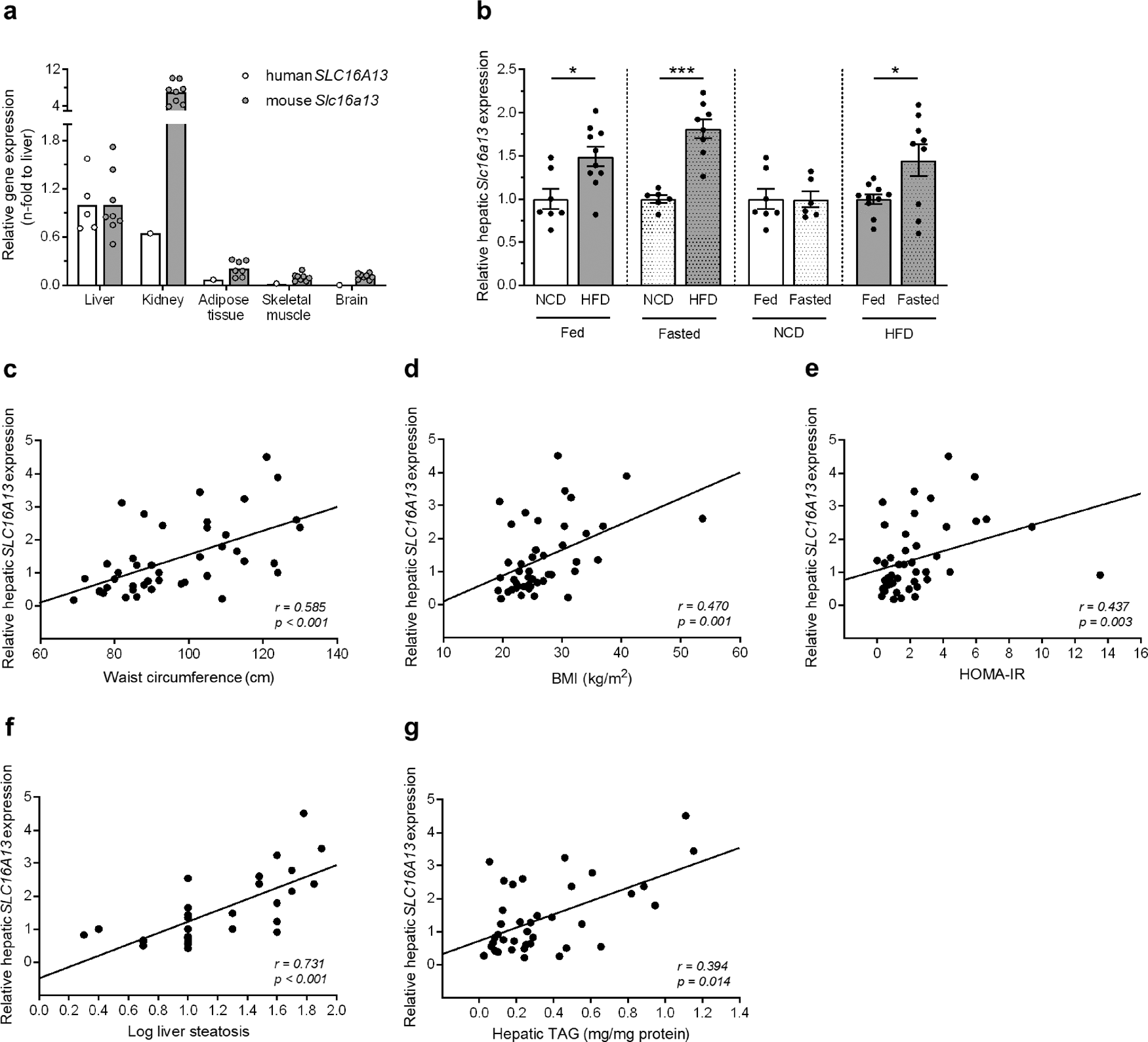
Deletion of the diabetes candidate gene Slc16a13 in mice attenuates diet-induced ectopic lipid accumulation and insulin resistance | Communications Biology

Beta-cell specific Insr deletion promotes insulin hypersecretion and improves glucose tolerance prior to global insulin resistance | Nature Communications

Tropomodulin3 is a novel Akt2 effector regulating insulin-stimulated GLUT4 exocytosis through cortical actin remodeling | Nature Communications
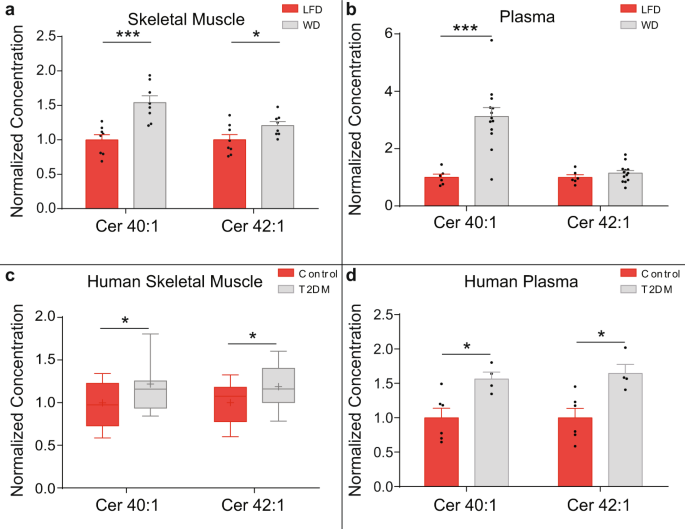
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications
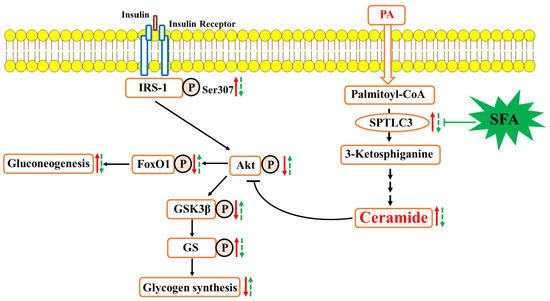
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Sulforaphane Prevents Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Blocking Serine Palmitoyltransferase 3-Mediated Ceramide Biosynthesis
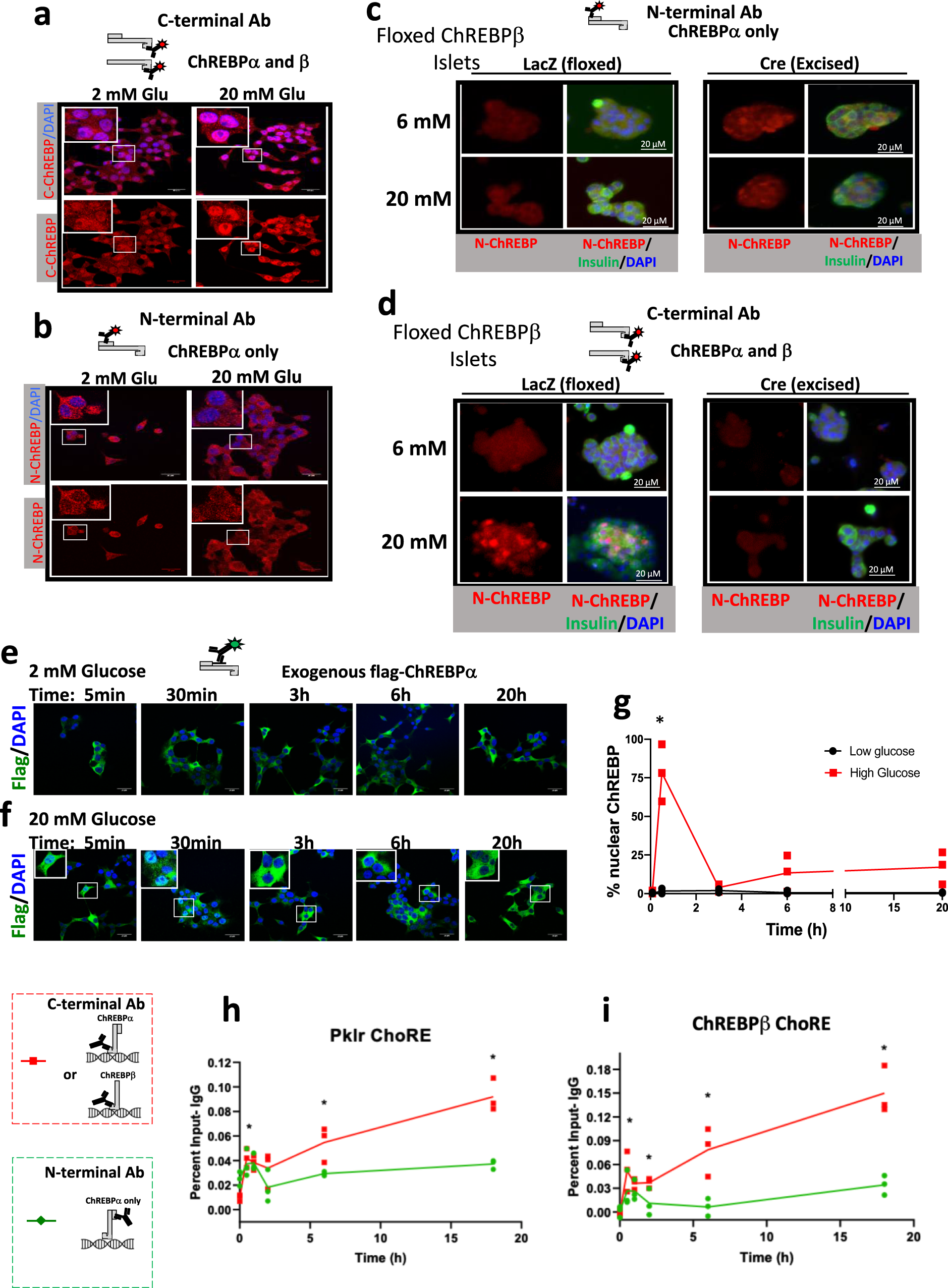
Maladaptive positive feedback production of ChREBPβ underlies glucotoxic β-cell failure | Nature Communications
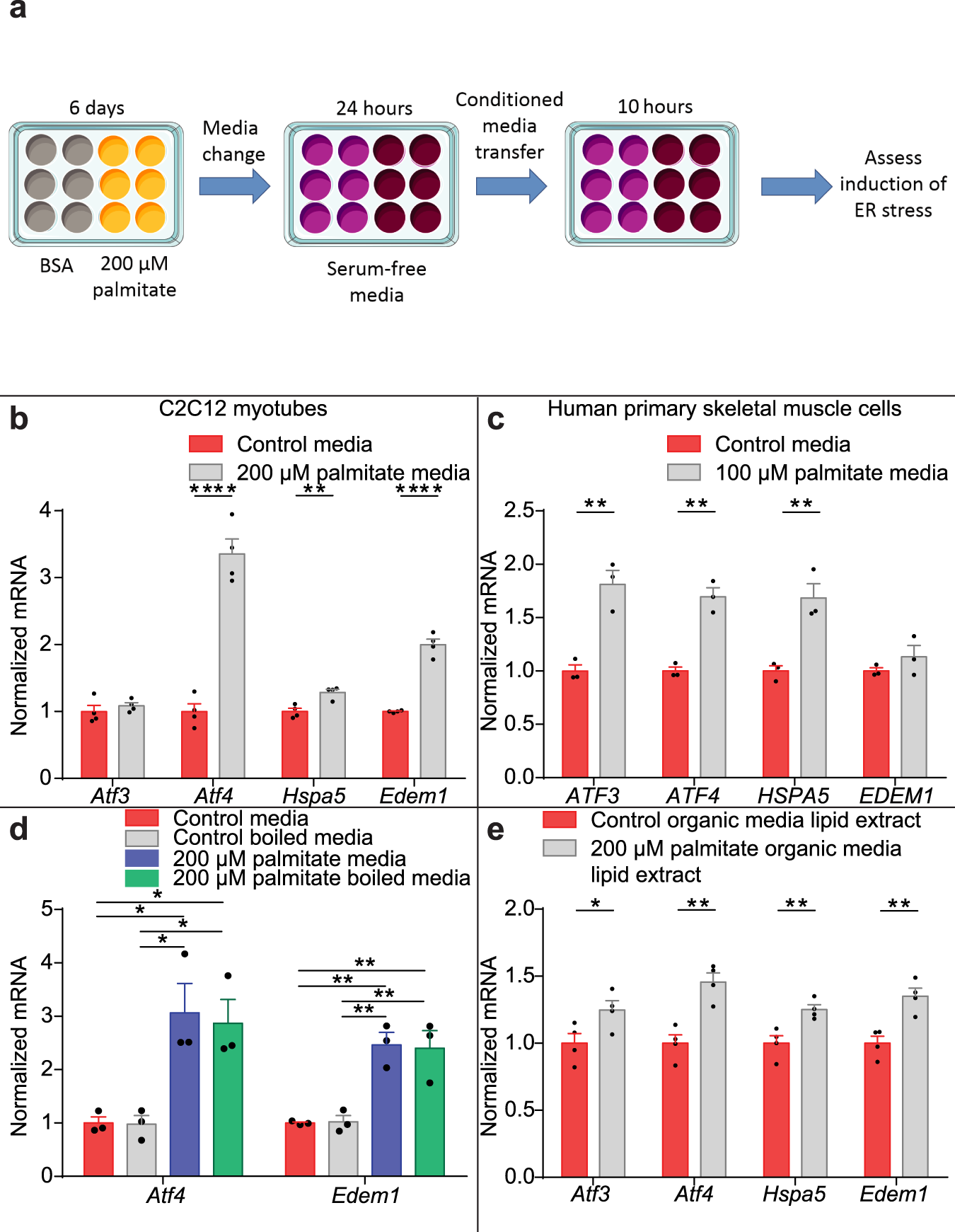
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications

Dihydroceramide- and ceramide-profiling provides insights into human cardiometabolic disease etiology | Nature Communications
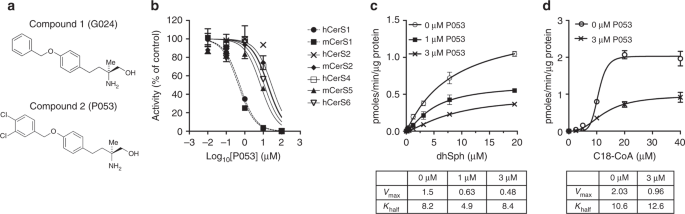
A selective inhibitor of ceramide synthase 1 reveals a novel role in fat metabolism | Nature Communications