
If g(1)=1, g(5)=-8 and int_1^5 g(x) dx = -9, evaluate the integral int_1^5 x g'(x) dx. (By Parts!) - YouTube

OneClass: Use the values "Integral 6,0" f(x) dx = 9 & "Integral 6,0 g(x) dx = 4 to evaluate the d...
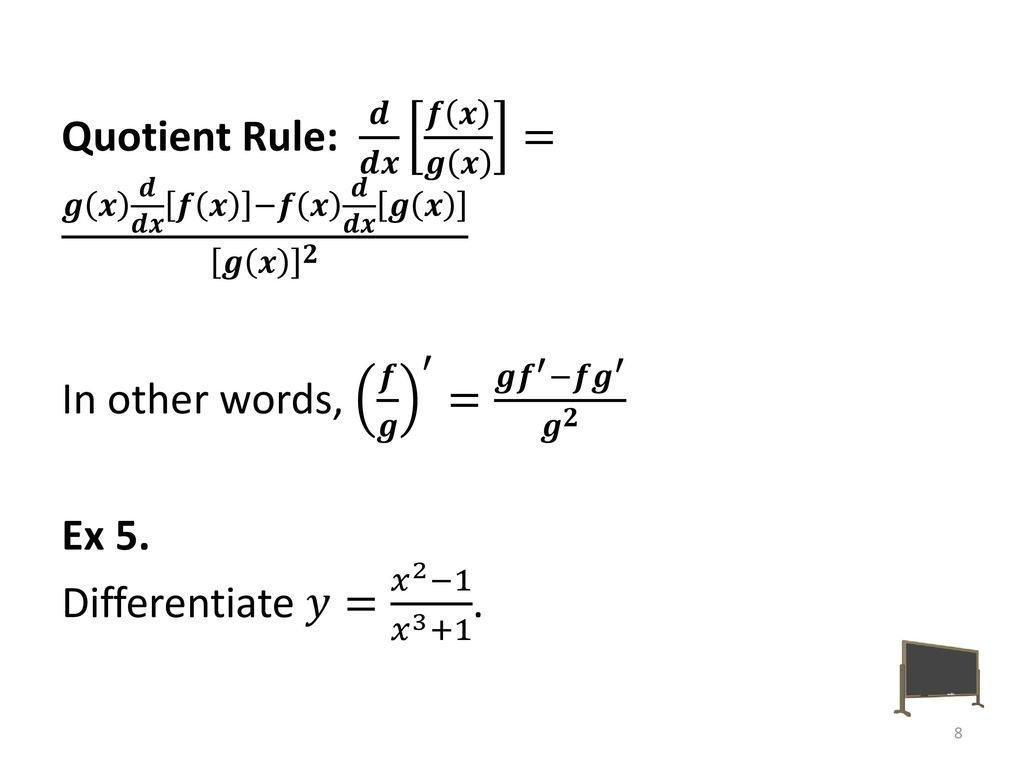
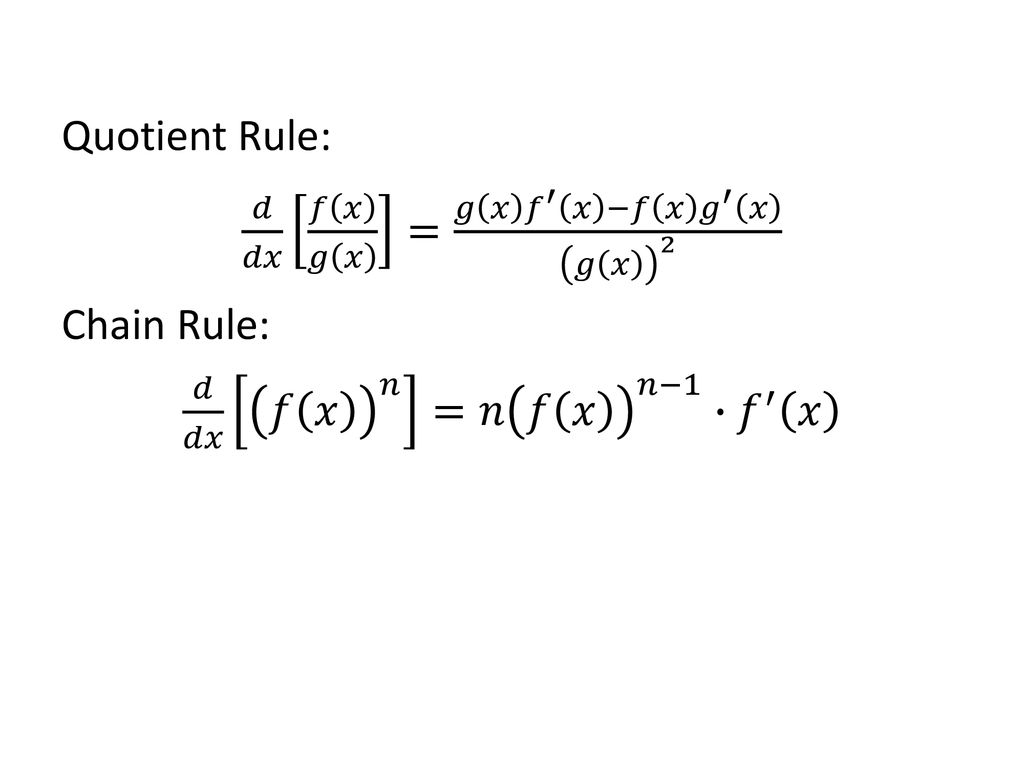
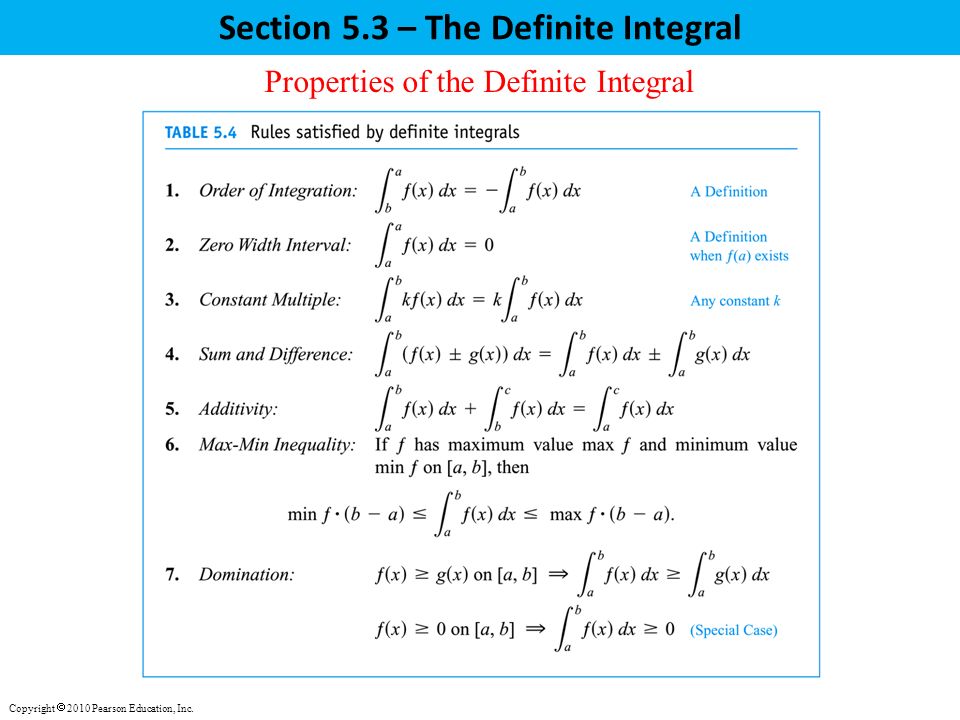
Math /3.2 - Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions and the Product and Quotient Rules. - ppt download
![int(-(pi)/(2))^((pi)/(2)) (f(x) + f(-x))(g(x) - g(-x)) dx where f(x) and g(x) are continuous functions on [-(pi)/(2), (pi)/(2)] int(-(pi)/(2))^((pi)/(2)) (f(x) + f(-x))(g(x) - g(-x)) dx where f(x) and g(x) are continuous functions on [-(pi)/(2), (pi)/(2)]](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/web-thumb/642816916_web.png)
int(-(pi)/(2))^((pi)/(2)) (f(x) + f(-x))(g(x) - g(-x)) dx where f(x) and g(x) are continuous functions on [-(pi)/(2), (pi)/(2)]

9. Suppose that ƒ an d g are integrable and that2∫1ƒ(x) dx = -4, 5∫1ƒ(x) dx = 6, 5∫1 g(x) dx = 8. - YouTube

Derivative of Definite Integrals with Two Limits d/dx ∫_(√x)^(x^2)·〖cost^2 dt〗 Chain Rule FTC1 - YouTube
AP Calculus AB Sample Student Responses and Scoring Commentary from the 2018 Exam Administration: Free-Response Question 3



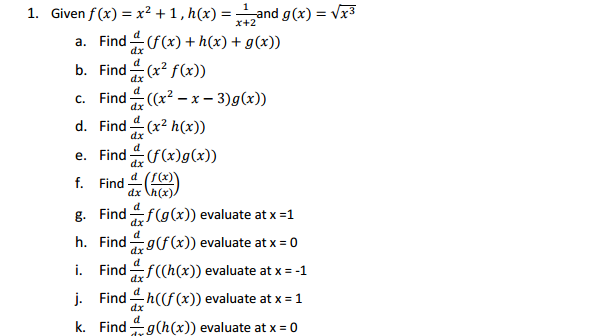

![Calculus POD #19 Use the Table to find the Derivative d/dx[ 4x - 3g(x) ] evaluated at x=4 - YouTube Calculus POD #19 Use the Table to find the Derivative d/dx[ 4x - 3g(x) ] evaluated at x=4 - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Nu1fK2RQ1qs/maxresdefault.jpg)

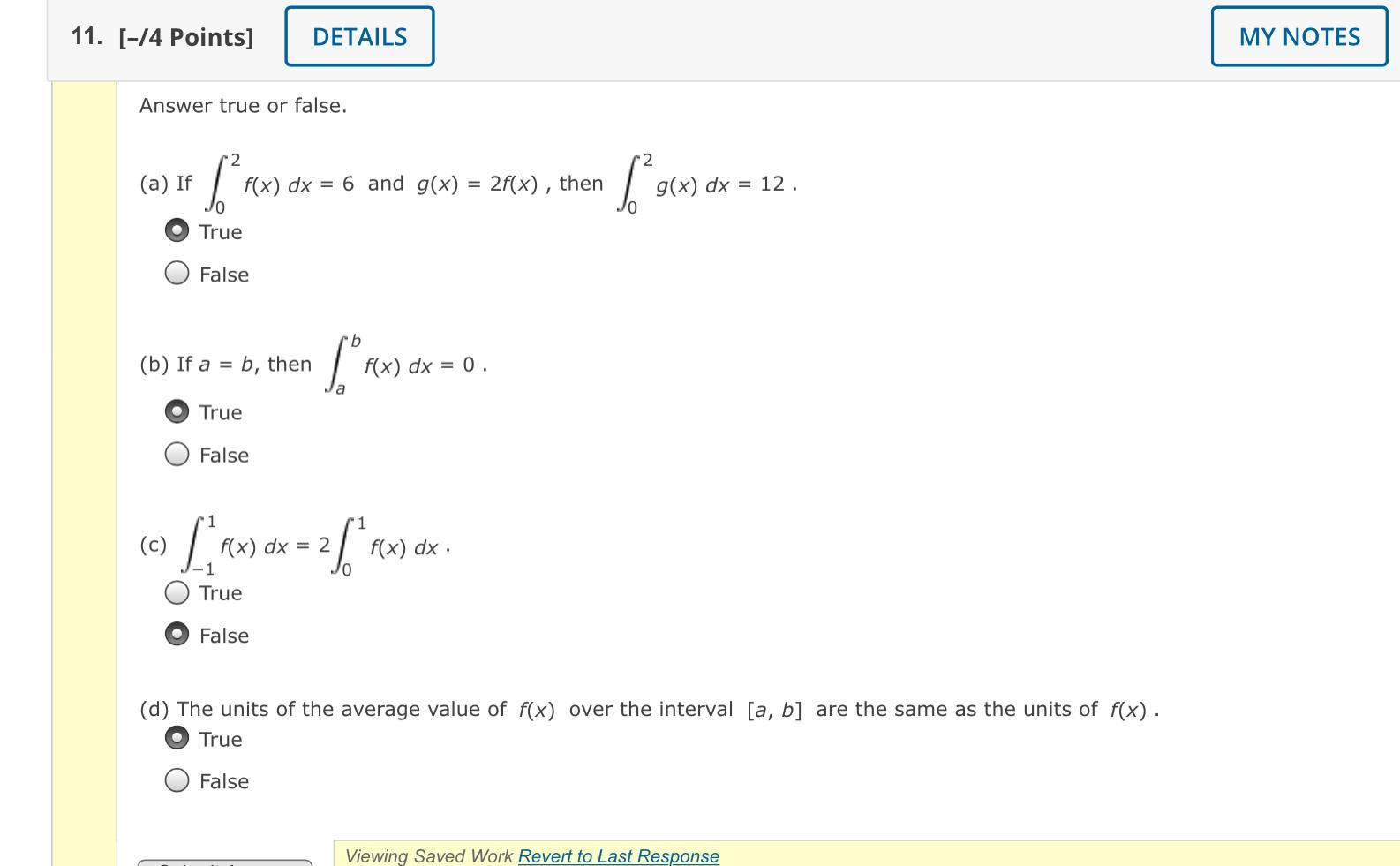



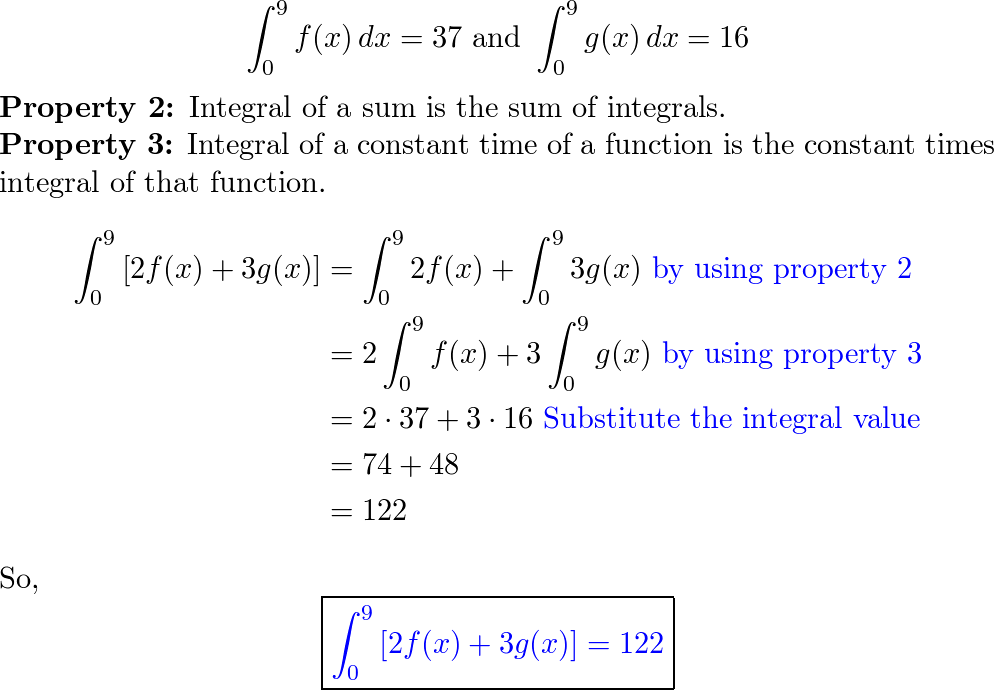
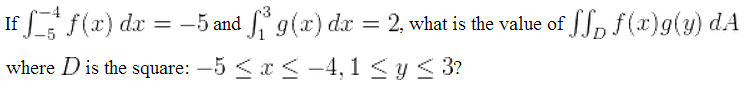
![Proof - the Derivative of Sum and Difference of Functions: d/dx[f(x)+g(x)] - YouTube Proof - the Derivative of Sum and Difference of Functions: d/dx[f(x)+g(x)] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Lmmx6djsdtU/maxresdefault.jpg)
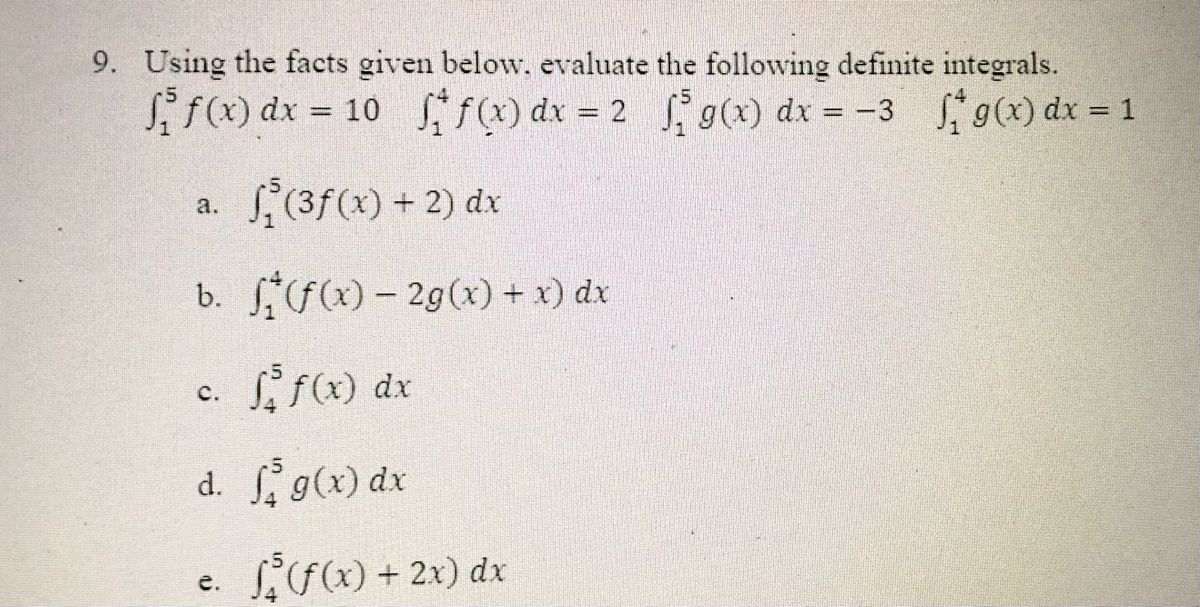
![If intf(x)dx = g(x) , then intf^-1(x) dx is[Where C is constant of integration] If intf(x)dx = g(x) , then intf^-1(x) dx is[Where C is constant of integration]](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1070169_996049_ans_03ad908bf73849ccab31e8a55b6893a4.jpeg)
